AY Honors/Computers and Mobile Devices/Answer Key
Skill Level
1
Year
2021
Version
06.03.2026
Approval authority
North American Division
1
Computers (laptops and desktops) include:
Personal computers with Windows, Macs with iOS, personal computers with Linux, Chromebooks with Chrome OS
Devices include: Android, Windows, and iPad tablets, iPhones and Android OS phones, Smart homekit devices, such as Alexa and Google assistant.
2
2a
A computer case, also known as a computer chassis, tower, system unit, or cabinet, is the enclosure that contains most of the components of a personal computer.
2b
A computer display, monitor or screen is a computer peripheral device capable of showing still or moving images generated by a computer.
2c
A computer keyboard is a peripheral modelled after the typewriter keyboard. Keyboards are designed for the input of text and characters, and also to control the operation of the computer. Physically, computer keyboards are an arrangement of rectangular or near-rectangular buttons, or "keys". Keyboards typically have characters engraved or printed on the keys; in most cases, each press of a key corresponds to a single written symbol. However, to produce some symbols requires pressing and holding several keys simultaneously, or in sequence; other keys do not produce any symbol, but instead affect the operation of the computer, or the keyboard itself.
- Roughly 50% of all keyboard keys produce letters, numbers or signs (characters). Other keys can produce actions when pressed, and other actions are available by simultaneously pressing more than one action key.
2d
A mouse is a pointing device that is dragged across a flat surface to move the cursor on a computer screen, typically having buttons that are pressed to control functions.
A touchpad or trackpad is a pointing device featuring a tactile sensor, a specialized surface that can translate the motion and position of a user's fingers to a relative position on the operating system that is made output to the screen. Touchpads are a common feature of laptop computers
2e
CPU is an acronym that stands for "Central Processing Unit." This is the "brain" behind a computer, and is where all the arithmetic, logic, and program flow is performed.
2f
RAM is an acronym that stands for Random Access Memory. "Random access" means that the contents of the memory can be accessed in any random order. The term was originally coined to differentiate it from serial memory (such as data stored on a magnetic tape). The contents of a serial memory could only be accessed sequentially. RAM is a volatile memory, which means that when the power is turned off, the information stored there is lost.
RAM can be accessed very quickly by the computer. Its contents can be both read and written. Most programs on a computer are loaded into and executed from RAM. RAM is also used as "scratch space" where the computer stores the results of calculations.
2g
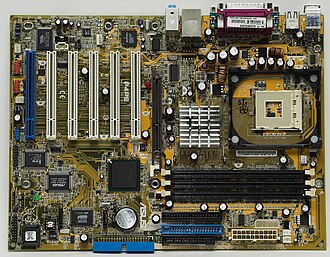
The mother board is located inside the main unit and contains the core circuitry of the computer, including the CPU. It also contains "slots" that other circuit cards such can be plugged into to add extra functions to the computer, such as a modem, networking, video acceleration, or a television tuner. The functions provided by these add-on cards (or daughter cards) are often absorbed into the motherboard as new technology is introduced. Modems, networking, sound, graphics, hard drive controllers, and USB adapters are examples of technology introduced as add-on cards, but now commonly found on the motherboard.
2h
A hard drive is a nonvolatile data storage device. It works by the same principals as a floppy disc, except that it is much faster, has much greater storage capacity, and is usually not removable from the computer. Most hard drives consist of several aluminum platters stacked on a spindle. The platters (or disks) are coated with a material whose magnetic properties are easily detected (for reading) and changed (for writing). The computer's operating system is usually stored on the hard drive as are most of the other programs the computer runs. Data stored on a hard drive will not be destroyed if the computer is turned off.
An internal drive is a storage device that is installed inside the computer. The advantage of an internal drive is that it takes up less space and is generally more reliable than an external drive.
2i
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It is a convenient method of interfacing many different devices to a computer. USB devices include cameras, printers, flash memory drives, external hard drives, music players, and many others. USB ports are located on the back, front, or both sides of a computer, and sometimes even on computer monitors. A USB device is simply plugged into the port, and the computer recognizes the device and prepares it for use.
2j
Modem stands for Modulator/Demodulator, and it a hardware device which allows computers to communicate with one another over a telephone line (or some other audio channel). A network card serves the same function except that it connects to a computer network (such as ethernet) and is much, much faster than a modem. Modems are used for "dial-up" internet connections, and network cards are used for "broadband" internet connections.
The Wi-Fi card (usually only a Wi-Fi indicator light is visible) are the units that communicate directly with technologies that bring internet to the computer.
2k
The component that supplies power to a computer. Most personal computers can be plugged into standard electrical outlets. The power supply then pulls the required amount of electricity and converts the AC current to DC current. The power cable plugs into the wall and carries electricity to the power supply unit. On a desktop it is "three-pronged" at the computer chassis.
2l
2m
3
3a
A display device which allows the user to interact with a computer by touching areas on the screen. There are resistive and capacitive screens. Resistive screens work as they recognize the pressure of the finger on the screen. Capacitive screens respond to the natural electricity the body produces.
3b
3c
3d
3e
3f
3g
3h
3i
3j
3k
3l
3m
3n
3o
3p
3q
3r
3s
3t
4
5
5a
i
ii
iii
iv
Memory can be determined by examining system setting screens, which vary by OS.
v
Symbols on the screen indicate 1-4 bars or dots. The more bars, the stronger the signal and, thus, more reliable (and faster) the internet connection speed between your computer and the internet.
vi
Laptops and Chromebooks have a battery so are often charged; then they can be used without being plugged in. The battery life indicator displays how many minutes are left before the system dies.
5b
i
Operating systems vary dramatically by phone/tablet manufacturer. Search on the internet for your type of device to discover HOW to determine this information. Usually it is in a Setting, General tab, About tab, or similar screen.
ii
iPhone - Settings App, General Tab, backup and storage option.
iii
iPhone - Settings App, General Tab, backup and storage option.
iv
Most tablets and phones indicate a battery icon with 3-5 "segments" with one or more filled to illustrate battery life still available.
v
6
6a
6b
7
7a
A digital camera is a device which digitally captures and stores an image in the form of a photograph. The photograph can then be transferred to a computer where it can be stored, transmitted to other computers, or digitally manipulated.
7b
An external drive is a storage device that is connected to a computer vía a USB (or other) port. The drive itself remains outside the computer. The advantage of an external drive is that it is easier to install and it can be moved from one computer to another. This feature can be used for physically transporting large amounts of data between computers or securing the data in an off-site location.
It is used to ADD data storage to a computer OR allow you to carry data from one device/computer to another. Usually runs more slowly than internal HDD. Lots of photos and documents can be stored (depending on the gigabytes of storage on the drive).
7c
7d
7e
7f
A printer is a peripheral device which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text, usually on paper.
Ink Jet Printer
Most current inkjets work by having a print cartridge with a series of tiny electrically-heated chambers. To produce an image, the printer runs a pulse of current through the heating elements. A steam explosion in the chamber forms a bubble, which propels a droplet of ink onto the paper (hence Canon's tradename for its inkjets, Bubblejet). When the bubble condenses, surplus ink is sucked back up from the printing surface. The ink's surface tension pumps another charge of ink into the chamber through a narrow channel attached to an ink reservoir.
Compared to earlier consumer-oriented printers, ink jets have a number of advantages. They are quieter in operation than impact dot matrix or daisywheel printers. They can print finer, smoother details through higher printhead resolution, and many ink jets with photorealistic-quality color printing are widely available.
The disadvantages of inkjets include flimsy print heads (prone to clogging) and expensive ink cartridges (sometimes costing US$30 – $40 or more). This typically leads value-minded consumers to consider laser printers for medium-to-high volume printer applications.
A common business model for inkjet printers involves selling the actual printer at or even below production cost, while dramatically marking up the price of the (proprietary) ink cartridges.
Laser Printer
A laser printer is a common type of computer printer that produces high quality printing, and is able to produce both text and graphics.
An electric charge is first projected onto a revolving drum. The drum has a surface of a special plastic or garnet. Electronics drive a system that writes light onto the drum with a laser. The light causes the electrostatic charge to leak from the exposed parts of the drum. The surface of the drum passes through a bath of very fine particles of dry plastic powder, or toner. The charged parts of the drum electrostatically attract the particles of powder. The drum then deposits the powder on a piece of paper. The paper passes through a fuser, which, with heat and pressure, bonds the plastic powder to the paper.
Laser printers are the workhorse printer of the business world. They are capable of producing very high quality prints very cheaply. Although most laser printers only work in black and white, some models can also produce color prints. Because of their speed and economy, laser printers have largely replaced all other types of printers except ink jet and thermal printers.
7g
A scanner is a device which is used to digitize a two-dimensional image, such as a printed photograph, a page from a book, or a store receipt. 3D scanners are now becoming common.
7h
A projector or image projector is an optical device that projects an image onto a surface, commonly a projection screen. Most projectors create an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens, but some newer types of projectors can project the image directly, by using lasers.
7i
7j
Smart environment devices link computers and other smart devices to everyday settings and tasks. Smart environments include smart homes, smart cities and smart manufacturing. At the time of this answer key, Alexa and Siri were significant "voices" for series of devices used in homes.
7k
An input device is any hardware device that sends data to a computer, allowing you to interact with and control it.
An output device is any peripheral that receives data from a computer, usually for display, projection, or physical reproduction. Monitors and printers are two of the most commonly used output devices used with a computer.
8
8a
8b
Names for COMPUTER individuals include:
Top Choices
- Christopher Latham Sholes
- William Hewlett and David Packard
- Carol Shaw
- Robert Kahn and Vinton Cerf
- Tim Berners-Lee
- Ed Roberts (Computer Engineer)
- Adam Osborne
- Martin Cooper
- Douglas Engelbart
- Katherine G. Johnson & Dorothy Johnson Vaughan
- Steve Jobs
- Steve Wozniak
- Bill Gates
- Linus Torvalds
Others
- Jean Bartik
- Konrad Zuse
- John Atanasoff
- Grace Hopper
- Joseph Marie Jacquard
- Gottfried Leibniz
- Thomas T. Goldsmith, Jr. and Estle R. Mann
- E. A. Johnson
- Ralph H. Baer
- Robert Noyce
- Nolan Bushnell or Steve Russell (computer scientist)
- Dov Moran
8c
9
9a
9b
9c
Sending notes home/speaking with parents about the potential value to their family structure if they manage this discussion well is worth the extra effort. TThis conversation can be the HIGHLIGHT for the young learners as they bring together with their parent their tech and Jesus. This is a deep time with lasting significance, if prepared and planned for well. Doing a, b and c in sequence and through positive non-judgmental dialogue is essential.
10
- a. When did you first start using computing devices for work? What type was it?
- b. What kind of computer do you use at work? At home? Why do you use those particular computer systems?
- c. Which computing activities that you do during a typical week are best done on a computer? On a mobile device? Evaluate reasons for each decision.
- d. What are things you do on mobile devices that you used to need a computer for?
- e. How do you balance your screen time with your “real world” interactions with people? What advice would you give about how to choose screen time?
- f. What Bible counsel or stories do you try to remember when balancing your screen time and entertainment choices?
IF “D & E” here come in close proximity to the learner’s evaluation of their screen-time, there is incredible family potential heart-spiritual value here. Prepare well, strategize timing of implementation well!
11