Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Porifera and Cnidaria/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "300px") |
(Created page with "{{clear}}") |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 13:38, 19 April 2021
Nivel de destreza
2
Año
2012
Version
03.02.2026
Autoridad de aprobación
División Sudamericana
1
2
3
Sponges are multicellular animals with an outer and inner membrane (the Ectoderm and Endoderm respectively), with a non-cellular jelly-like matrix between these cellular layers. Sponges have specialized Chanocytes, cells with a flagellum to create a current to draw water over special hair-like projections in a ring around the flagellum. Sponges gain structural strength from spicules, which in some form a type of skeleton. Spicules can be made of protein fibers, silica (glass) or calcium carbonate. Sponges are sessile, they do not move (though certain embryonic stages are capable of movement). Sponges do not necessarily have any particular symmetry to their body form.
4
5
6
7
8
9
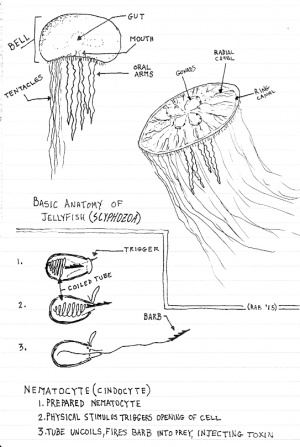
Use a picture of a Jellyfish as a guide, or try to draw from a live jellyfish at an aquarium or zoo.
10
Coral reefs serve as nurseries and living quarters for numerous difference species of marine animals, and thus play a very important role in ecological webs. They also provide shelter against storms to some coastal areas, and are a vital part of tourism in many tropical countries.
11
The Great Barrier Reef, off the coast of Queensland, Australia, is considered the largest coral reef in the world, at more than 1400 miles long, and covers approximately half the total land area of the state of Texas. Other large reefs include the Red Sea coral reef, at more than 1100 miles long, and the Florida Keys reef, at more than 200 miles long.