Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Bacteria/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "<noinclude>") |
(Created page with "</noinclude> ==Referencias== Categoría:Libro de Respuestas de Especialidades JA <noinclude>") |
||
| Line 200: | Line 200: | ||
<!-- 10. Nombrar cinco enfermedades provocadas por bacterias y algunas precauciones que se debe tener para evitarlas. --> | <!-- 10. Nombrar cinco enfermedades provocadas por bacterias y algunas precauciones que se debe tener para evitarlas. --> | ||
| − | + | {{clear}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 04:50, 5 April 2021
1
2
Flagellum: A hair- or whip-like appendage, used for motility
3
4
5
Certain bacteria may reproduce through budding, a process where a small bud forms on a parent bacteria, genetic material is transferred to the bud, and then it separates.
Some bacteria, including some of the Firmicutes bacteria, create two complete daughter cells inside the parent, then the parent breaks open and dies, releasing the two new bacteria cells.
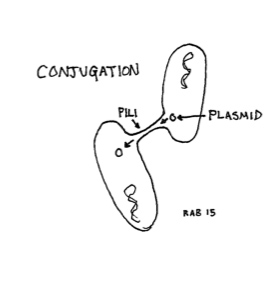
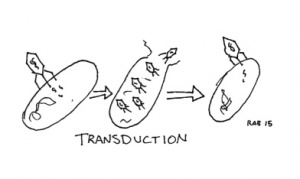
Given that bacterial reproduction is primarily through forms of fission (division), there is no change in genetic material aside from mutation. However, Bacteria do have other ways to transfer genetic material, though not quite analogous to sexual reproduction.
Transduction: A bacteriophage (a virus that uses bacteria as a host) may pick up some pieces of genetic material from a previous host and incidentally transfer it into a new bacterial host.
Transformation: Bacteria may pick up fragments of genetic material from their environment, usually left by dead bacteria.
6
Categories of Autotrophs:
7
8
9
10
Typhoid Fever (Salmonella typhi) - Transferred through contaminated water.
Prevention: Vaccination. Also, for the unvaccinated, in areas where Typhoid may be present, it is best not to consume fresh fruits and vegetables that have been washed with untreated water, and best not to drink water that isn’t bottled (also be wary of ice, as it is usually made from local water).
Cholera (Vibrio cholera) - Transferred through water contaminated with bodily fluids.
Prevention: In areas where cholera may be prevalent, wash hands thoroughly, avoid fresh fruit or vegetables unless you can peel them yourself, only eat cooked food, do not drink the local water.
Tetanus (Clostridium tetani) - Transferred through contamination into wounds.
Prevention: Vaccination (note that tetanus vaccinations need updated relatively frequently compared to many other types of vaccinations) Also, be careful around rusty and dirty objects that can cause puncture wounds or cuts. Wash wounds thoroughly and apply a surface antiseptic. Leave deeper wounds open to drain (seek medical attention as appropriate).
Tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) - Transferred through droplets in coughs and sneezes.
Prevention: Use caution in areas where tuberculosis is common. Wear face masks, wash hands, do not touch hands to face or mouth, try to avoid enclosed spaces with those that may be infected, work in open, well ventilated areas.
Lyme Disease (Borrelia burgdorferi) - Transferred through the bite of certain ticks.
Prevention: Avoid or use caution in areas that may be infested with ticks (tall grasses, thick undergrowth, etc). Wear long pants and long sleeves, tuck pant legs into boots or socks, use insect repellents with DEET, check frequently for ticks, remove ticks carefully, apply surface antiseptic.
11