For the purposes of the sailing honor we will focus in the rules of the road that apply to small sailing boats.
It is important to note here that you are responsible for learning the rules and regulations that apply to whichever boat you are operating in the country and state or province where you are operating the boat.
There are five basic rules of the road for small sailing boats to decide who has the "Right-of-Way" so that each boat's skipper (driver) will know what to do to avoid a collision.
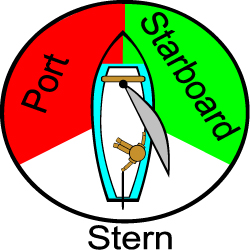
When sailing the words "left" and "right" in reference are replaced with "port" and "starboard". It is important to remember which is which since the rules of the road for sailing rely on using these words to assign right-of-way.
You might be able to remember this by noticing that the letter "R" appears twice in the word "starboard", and only once in "port". Then since "right" begins with "R", you will know that the right hand side of the boat when facing forward is the starboard side.
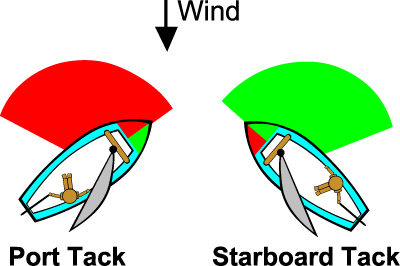
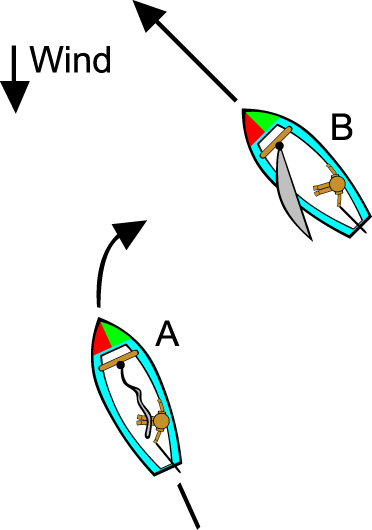
The next item to remember is the word "tack" and how it is used to describe which side of the boat the wind is blowing from. As seen in the illustration below, if the wind is coming from the right hand side of the boat, and the sail is on the left side, the boat is on a starboard tack. When the wind and sail are reveresed, the boat is on a port tack.
Rule Number 1:
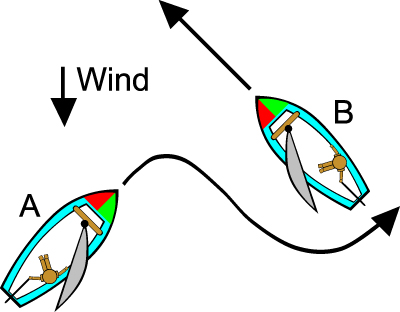
When two sailboats are approaching each other and are on different tacks, the boat on the starboard tack has the right-of-way over the boat which is in the port tack. An easy way to remember this is to think about power boat lights. At the front the boat has red on the port (left side) and green to the starboard (right). If you are approaching a boat and can "see" the red light, then the other boat has the right of way. (small sail boats rarely have the actual lights, but you can imagine them)
In the illustration below, boat "A" on the port tack, must turn to avoid boat "B" on the starboard tack.
Rule Number 2:
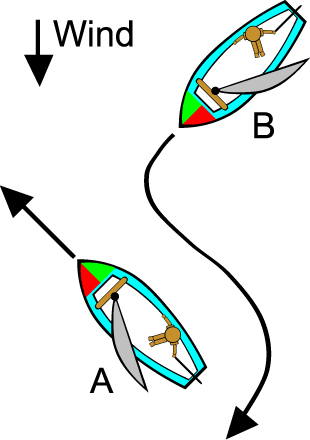
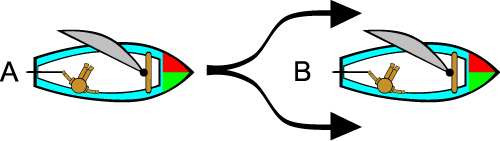
When two sailboats are approaching each other and are on the same tack, the leeward boat has the right-of-way over the windward boat. Another way to say this is to say that the boat closer to the wind source must keep clear. The boat further from the wind source has the right-of-way.
In the illustration below, boat "B" is the windward boat and must turn to avoid boat "A" which is leeward.
Rule Number 3
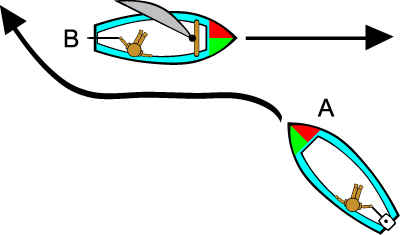
A sailboat that is staying on a tack has the right-of-way over a sailboat that is tacking or gybing. A simpler way to say this is to say "make sure you have room to complete a tack or a gybe without interfering with any other boats before doing so". Make sure that you can see clearly in all directions to ensure you have room.
In the illustration below, boat "A" must ensure that it leaves plenty of room to avoid boat "B", who has the right-of-way, since boat "B" is continuing on its tack. However, in the event that boat "A" was unable to tack due to the proximity of "B", remember that "A" is the leeward boat so therefore could tell boat "B" to give room to tack, but would lose this right of way as soon as they actually began to tack.
Rule Number 4
Any sailboat that is overtaking a slower boat from behind must steer clear of the slower boat and give right-of-way. The slower boat should hold its course and allow the faster boat to pass.
In the illustration below, boat "A" is a faster boat, and must steer around the slower boat "B", who should remain on the same course.
Rule Number 5
Most of the time sailboats have the right-of-way over power boats. Since most powerboats are more easily maneuverable than sailboats, they must steer clear. This is not always the case however. Larger power boats are sometimes steering in the deep channel of the area, and cannot leave the channel. In this case the sailboat does not have right-of-way, and must avoid impeding the progress of the larger vessel. Many larger power boats cannot simply stop quickly or easily turn to avoid a small sailboat, so it is in the sailor's best interest to steer well clear of these larger boats.
In the illustration below, the powerboat "A" must turn to avoid the sailboat "B", who has the right-of-way.