Difference between revisions of "AY Honors/Model Railroad/Answer Key/es"
(Created page with "</noinclude> <!-- 2. Decir la diferencia en como los siguientes prototipos obtienen la fuerza motriz para operar: --> <noinclude>") |
(Created page with "</noinclude> <!-- 3. Conocer el nombre, escala, y el ancho de vía de ferrocarril de cuatro modelos de medidores. -->") |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{CloseReq}} <!-- 2 --> | {{CloseReq}} <!-- 2 --> | ||
{{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3}} | {{ansreq|page={{#titleparts:{{PAGENAME}}|2|1}}|num=3}} | ||
| − | <noinclude> | + | <noinclude></noinclude> |
| − | </noinclude> | + | <!-- 3. Conocer el nombre, escala, y el ancho de vía de ferrocarril de cuatro modelos de medidores. --> |
| − | <!-- 3. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
Revision as of 13:56, 2 May 2021
Nivel de destreza
2
Año
1967
Version
15.11.2024
Autoridad de aprobación
Asociación General
1
2
2a
2b
2c
3
4
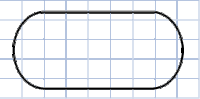
Oval
The simplest layout for a model railroad and the starting point for most designs. In this design, two straightaway segments are connected by a semi-circle at each end. This is also the only layout which can easily be created with sectional track without the use of a manufacturer-specific design. Curved sectional track is sold by radii (half the distance across the semi-circle) and a box of such track sections will almost always create exactly half a circle. The two straightaway sections will usually utilize multiple pieces of sectional straight track, as desired by the modeler.
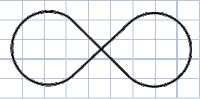
Figure-Eight
The second most common beginner's layout. This layout is best accomplished by purchasing it as a single set or following a manufacturer's layout design using their sectional track. The intersection in the center of the layout can either be accomplished by a piece of crossover track, or by elevating one track over the other. In the latter case, a set of piers or risers will be needed to raise the track at an appropriate rate.
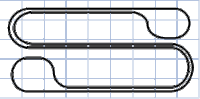
Twice-Around
A modification of the figure-eight, in which one end-loop is contained within the other. The crossover here is not at 90° like in the basic figure-eight example and can be accomplished by using a alternately angled crossover piece or by using elevated track to pass one track over the other. The twice-around layout design allows the train to run continuously for longer than the simple oval before reaching its starting point.
Point-to-Point
This design does not allow a train to run continuously indefinitely, as you might imagine most plans would allow. However, this is the design that most closely resembles real-life railroad operation, since real-life railroads run across country, not in loops or circles. You can construct more elaborate yards at each end in order to enjoy the complexities of real-world operation.
Out-and-Back
This design approximates real-world operation, as each train must make a journey before it returns to the yard from which it originated. Although real freight never returns to its origin the same way it left, this arrangement does allows you to concentrate your time and resources on one yard instead of the two required in a Point-to-Point design (above).
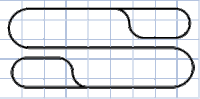
Loop-to-Loop
This design diverges from realistic operation, but does allow the operator to interact with a continuous-running train. A yard can be added in the middle of the layout to simulate freight coming in from each direction. When modeling with two-rail scales, such as HO and smaller, special wiring will be required to insulate each loop from the rest of the line and allow the direction to be reversed on the mainline.
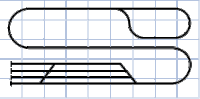
Dog Bone
This design is similar to the loop-to-loop design, but allows for continuous running without intervention from an operator. In addition, the two tracks running side-by-side simulate the double-track lines often seen in real life.
Twisted Dog Bone
This design is adds additional length to the mainline featured in the basic dog-bone design (above). Keeping one or both of the end-loops out of sight allows this layout to very realistically simulate the long distance running of a real railroad.
5
Cleaning & Checking Basic Trackwork
Most model railroads receive power for their electric motors through the tracks they run on. Thus, track must be kept clean and free of even the smallest obstructions. A train running on a dirty track does not operate smoothly or realistically, or may not run at all! The space between rails must also be maintained, though this is more of an issue when individual rails and ties have been laid down by hand. Sectional track usually maintains its proper gauge (space between the rails). Rail cleaning solution can be safely wiped across model track and track-cleaning cars are also available for running around the layout and cleaning hard-to-reach places.
Checking Wheels and Couplers
Locomotives and cars are kept rolling along together by various types of 'couplers.' These can be very tiny on the smaller model railroad scales, but in any case, they must be kept clean and properly hooked together for a train to run along smoothly. Another common problem is derailment when a car's wheels come off the track. This can also be harder to detect on smaller scale trains, but it will eventually get noticed as cars may tip completely off the track. Nevertheless, derailment is the most common operating problem encountered and should be one of the first possibility to check when things are going wrong.
Lubricating Engine Drive Mechanisms
Most model locomotives are powered by electric motors which involve a minimum of moving parts. There are typically tiny gears used in transferring the turning motor's power to the drive wheels of the locomotive. These are easily lubricated with special grease and/or oil available from a hobby supply store. Be careful to follow both the engine and lubricant manufacturers' instructions. Most wheels on other non-powered cars do not need to be oiled or greased except in rare cases.
Detailing Scenes & Structures
Model structures and landscape gather dust, making them look less realistic. These elements of a typical layout should be well anchored with adhesive when they are first installed so that their surfaces can be brushed clean, repainted, re-weathered and even vacuumed. In addition, its fun and rewarding to keep a layout fresh by installing new structures or creating new track-side scenes once your basic modeling is complete.
Testing Electrical Connections
Most model locomotives receive their power from the tracks below through one or more of their wheel sets. Since these wheels are turning, they transmit their power through stationary metal brushes that maintain contact with the tiny axle running between these wheels. These brushes should be kept clean and checked whenever an electrical problem is suspected. In addition, the wires which run from the operator's power pack to the rails themselves can become tangled, shorted out (when they inadvertently touch each other), or disconnected all leading to potential breakdown in the power supplied to the model railroad. A simple electric meter available from a hobby or electronics store can help determine where a breakdown is occurring by testing (1) the output of the power pack directly, (2) the presence of power on the set of tracks where the train is located, or (3) at any control point in between, such as when a control panel switch is used to control power to different track sections.
Adjusting Turnouts, Switch Machines & Ground Throws
Turnouts (sometimes called 'switches') are used to send a train from one set of track to another. These are easy places for trains to become derailed because the wheels must pass over a series of changeable mechanical parts that are more complex than the simple two (or three) rails used elsewhere in the layout. The 'points' of a switch are moved between two different resting positions which determine what path the trail will take after it passes through the turnout. These points must rest securely against either the inside or outside rail and must not move otherwise. If the points are moved remotely, by an electrical signal sent from the control panel to a 'switch machine' next to the turnout, then this switch machine and its associated wiring must be in good working order. If the switch is operated by hand using a small lever or 'ground throw' next to the turnout, then the ground throw needs to be kept clean and lubricated and able to move the points the full distance between their two desired positions.
6
6a
6b
6c
6d
6e
6f
7
7a
7b
7c
7d
7e
7f
7g
7h
7i
7j
7k
7l
7m
7n
7o
7p
7q
7r
7s
7t
7u
7v
7w
7x
7y
7z
7aa
7bb
7cc
7dd
7ee
7ff
7gg
8
- a. Ayudar en el montaje del marco exterior
- b. Instalar una sección de basalto
- c. Instalar una sección de vías
- d. Instalar al menos una vuelta, incluido el cableado
- e. Ayudar en la construcción del paisaje como árboles, rocas, montañas o el césped
- f. Hacer un modelo de edificio o estructura del tren
- g. Asistir en el cableado para el suministro de energía eléctrica a las vías
You can do this on your own, or as part of a club (either a group of Pathfinders earning the honor together, or as part of a model railroading club). Because there are a lot of requirements to meet here, it would be a good idea to make a checklist so you can be sure you have met each.
9